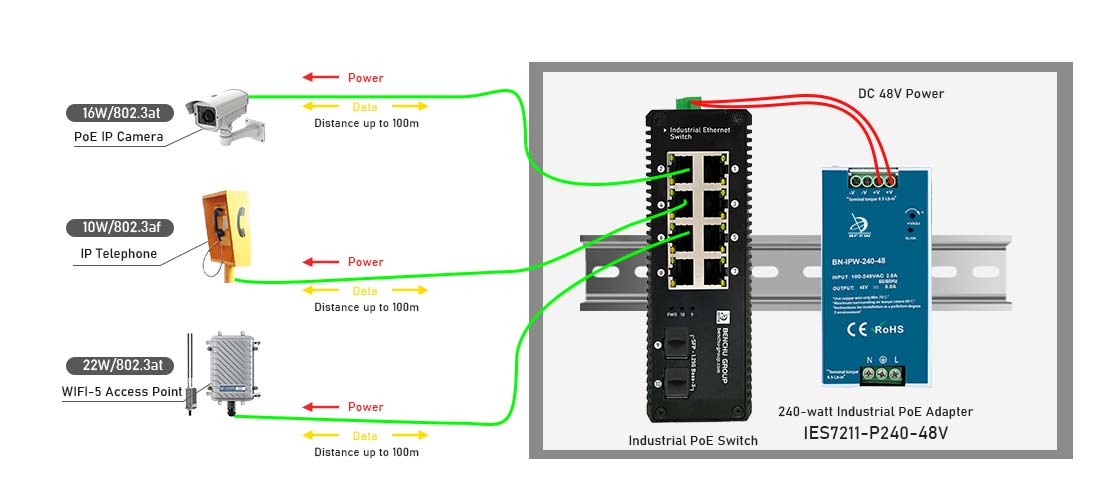
Una fuente de alimentación de riel DIN es un tipo de fuente de alimentación eléctrica diseñada para montarse en un riel DIN, un riel metálico estandarizado que se utiliza para montar equipos de control industrial en gabinetes. Las fuentes de alimentación de riel DIN se utilizan comúnmente en automatización industrial, sistemas de gestión de edificios y otras aplicaciones que requieren una entrega de energía confiable y compacta. A continuación se detalla qué es una fuente de alimentación de carril DIN y cómo funciona:
¿Qué es una fuente de alimentación de carril DIN?
Definición:
--- A Fuente de alimentación en carril DIN convierte una fuente de alimentación de entrada (CA o CC) en un voltaje CC regulado necesario para operar varios dispositivos electrónicos e industriales. Estas fuentes de alimentación están diseñadas para sujetarse de forma segura a un riel DIN, una tira de metal que normalmente se encuentra en paneles de control, gabinetes y gabinetes eléctricos.
Normalización:
--- Carril DIN: El nombre "DIN" proviene de la norma alemana "Deutsches Institut für Normung" (Instituto Alemán de Normalización). El tipo más común de carril DIN es el carril DIN de 35 mm (DIN EN 60715).
--- Compatibilidad: las fuentes de alimentación en riel DIN cumplen con estándares específicos de tamaño y montaje, lo que garantiza la compatibilidad con otros dispositivos montados en riel DIN, como disyuntores, relés y controladores.
Características clave:
--- Diseño compacto: Las fuentes de alimentación de riel DIN son compactas y ocupan poco espacio, lo que las hace adecuadas para recintos industriales y comerciales confinados.
--- Confiabilidad: Construido para soportar duras condiciones industriales, incluidos amplios rangos de temperatura, vibraciones y sobretensiones.
--- Escalabilidad: Fácilmente ampliable agregando múltiples unidades al mismo riel.
--- Salida regulada: Proporciona un voltaje de salida de CC estable y confiable, incluso bajo condiciones de entrada variables.
¿Cómo funciona una fuente de alimentación de carril DIN?
1. Etapa de entrada:
Las fuentes de alimentación en carril DIN aceptan una fuente de alimentación de entrada, que puede ser:
--- Entrada de CA: normalmente de 110 a 240 V CA, que es el voltaje de red estándar.
--- Entrada de CC: algunos modelos aceptan una entrada de CC, generalmente en un rango de 12 a 48 VCC, para uso en sistemas operados con baterías u otros entornos de CC.
--- La potencia de entrada pasa a través de filtros y rectificadores para eliminar el ruido y prepararla para la conversión.
2. Etapa de Conversión:
La fuente de alimentación utiliza una de las siguientes tecnologías para convertir la potencia de entrada en el voltaje de salida deseado:
Regulación lineal (menos común):
--- Diseño más simple, pero más grande y menos eficiente.
--- Normalmente se utiliza para aplicaciones de baja potencia donde la disipación de calor no es una preocupación.
Tecnología de fuente de alimentación de modo conmutado (SMPS) (más común):
--- Convierte la potencia de entrada mediante conmutación de alta frecuencia.
--- Ofrece alta eficiencia (hasta 90% o más) y tamaño compacto.
--- La entrada de CA se rectifica y filtra a CC, luego se convierte en CA de alta frecuencia. Esto pasa a través de un transformador para ajustar el voltaje, se rectifica nuevamente a CC y se regula.
3. Etapa de salida:
La salida CC regulada se suministra a los dispositivos conectados. Los voltajes de salida comunes incluyen:
--- 12 VCC
--- 24V DC (más común para sistemas de control industrial)
--- 48 VCC
La etapa de salida suele incluir protecciones como:
--- Protección contra sobretensión: evita que el voltaje excesivo dañe los dispositivos conectados.
--- Protección contra sobrecorriente: Limita la corriente para evitar daños en caso de cortocircuitos o sobrecargas.
--- Protección Térmica: Apaga la fuente de alimentación si se sobrecalienta.
4. Montaje y Conexiones:
--- Las fuentes de alimentación de carril DIN se montan en el carril DIN mediante clips o soportes de resorte. Las conexiones eléctricas se realizan mediante terminales de tornillo o conectores push-in para el cableado de entrada y salida. Una vez conectada, la fuente de alimentación distribuye energía a otros dispositivos en el mismo riel o dentro del sistema de control.
Aplicaciones de las fuentes de alimentación para carril DIN
Las fuentes de alimentación de carril DIN se utilizan en una amplia gama de aplicaciones, que incluyen:
1. Automatización Industrial:
--- Alimenta PLC (controladores lógicos programables), HMI (interfaces hombre-máquina), sensores y actuadores.
--- Utilizado en control de procesos y automatización de fábricas.
2. Sistemas de Gestión de Edificios:
--- Admite sistemas como HVAC, controles de iluminación y sistemas de seguridad.
3. Telecomunicaciones:
--- Proporciona energía estable para conmutadores de red, enrutadores y equipos de comunicación.
4. Transporte:
--- Utilizado en señalización ferroviaria, sistemas de control de tráfico y energía a bordo de vehículos.
5. Energías Renovables:
--- Admite controladores de paneles solares, cargadores de baterías y otros equipos de energía renovable.
6. IoT y sistemas inteligentes:
--- Alimenta puertas de enlace, dispositivos perimetrales y sensores de IoT en sistemas conectados.
Ventajas de las fuentes de alimentación en carril DIN
1. Compacto y Modular: Ahorra espacio y simplifica el cableado en paneles de control.
2. Fiable: Diseñado para un rendimiento de nivel industrial con protecciones robustas.
3. Flexible: Fácilmente ampliable o reemplazable sin rediseñar todo el sistema.
4. Fácil instalación: Montaje rápido y seguro en rieles DIN estandarizados.
5. Eficiencia energética: la alta eficiencia reduce el consumo de energía y la generación de calor.
Elegir una fuente de alimentación de carril DIN
Al seleccionar una fuente de alimentación de riel DIN, considere:
--- Rango de voltaje de entrada: Asegure la compatibilidad con su fuente de alimentación (CA o CC).
--- Voltaje y corriente de salida: cumpla con los requisitos de sus dispositivos.
--- Potencia nominal: elija una fuente de alimentación con suficiente potencia para admitir todos los dispositivos conectados.
--- Certificaciones: busque certificaciones como CE, UL o RoHS para cumplir con los estándares ambientales y de seguridad.
--- Condiciones ambientales: considere el rango de temperatura, la resistencia a las vibraciones y otros factores ambientales.
Conclusión
Una fuente de alimentación de riel DIN es un componente esencial en los sistemas de control industriales y comerciales, ya que ofrece energía CC confiable y regulada en un diseño compacto y modular. Funciona convirtiendo una entrada de CA o CC en una salida de CC estable, con protecciones para garantizar un funcionamiento seguro y eficiente. Ampliamente utilizadas en automatización, telecomunicaciones y sistemas de gestión de edificios, las fuentes de alimentación para carril DIN son conocidas por su facilidad de instalación, confiabilidad y flexibilidad en diversas aplicaciones.